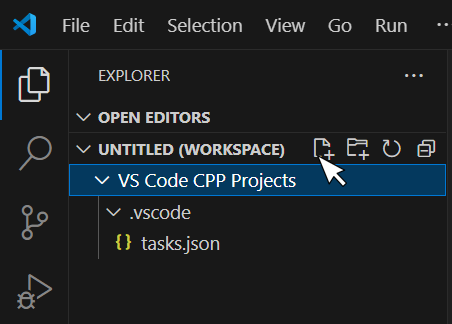
The first thing you must do is create a new C++ file. You have already added a folder to the workspace (see here for Windows or here for Linux). It is probably named “VS Code CPP Projects”. Click on the “Explorer” ![]() button in the Activity Bar on the left and select the folder “VS Code CPP Projects”. In the Side Bar that opens, click on the “New File”
button in the Activity Bar on the left and select the folder “VS Code CPP Projects”. In the Side Bar that opens, click on the “New File” ![]() option and create a file named “testingFile.cpp” (as shown in Figure 1).
option and create a file named “testingFile.cpp” (as shown in Figure 1).
Let’s now write the following (terrifying, and quite horrifying!) C++ program and try to execute it.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, World!" << endl;
cout << "Hallo, Welt!" << endl;
cout << "Bonjour, le Monde!" << endl;
return 0;
}
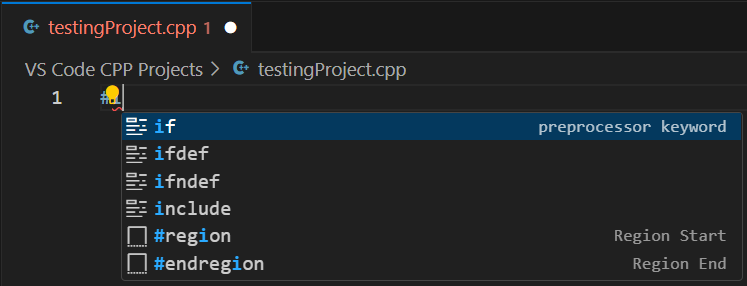
Let’s try to type the #include <iostream> statement. Type only the first two characters, “#i”, from the #include keyword. A popup window appears, as shown in Figure 2. This window contains all available C++ statements, and other items that begin with the characters “#i”.
Notice: You can highlight a selection by using the up and down arrow keys on your keyboard.
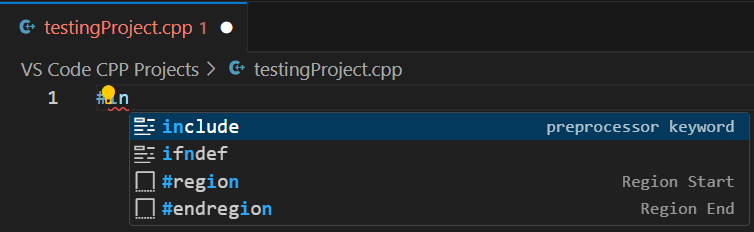
Type the third character, “n”, from the #include keyword. Now the options have become fewer. Select the option “#include” using the down arrow key from your keyboard (if necessary), as shown in Figure 3.
Hit the “Enter ⤶” key. The keyword #include is automatically entered into your program. Complete the statement by writing #include <iostream>. Then, continue typing the rest of the C++ program (as shown in Figure 4). Save the changes that you have just made. Your Visual Studio Code environment should look like this.
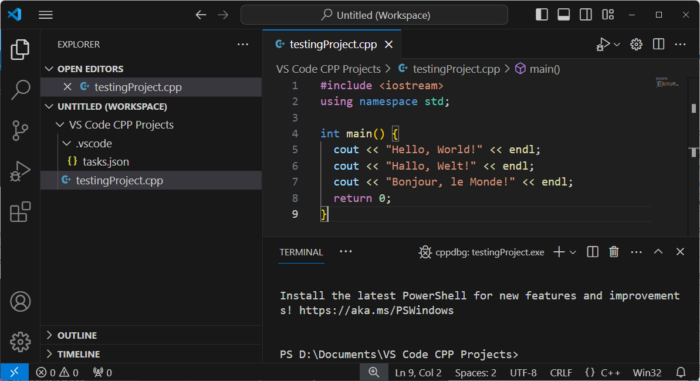
And now, let’s try to execute it! From the main menu, select “Run → Start Debugging”. The C++ program executes, and the output is displayed in the “Terminal” window, as shown in Figure 5.
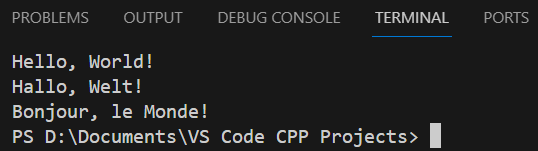
Notice: Alternatively, you can execute a file by hitting the F5 key.
Congratulations! You have just written and executed your first C++ program!
Now let’s write another C++ program, one that prompts the user to enter their name. Type the following C++ program into Visual Studio Code and hit F5 to execute the file.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string name;
cout << "Enter your name: ";
cin >> name;
cout << "Hello " << name << endl;
cout << "Have a nice day!" << endl;
return 0;
}
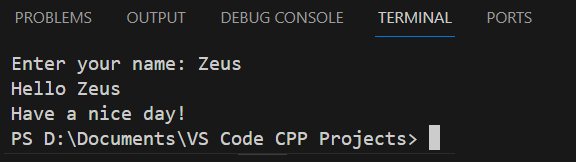
Once you execute the program, the message “Enter your name:” is displayed in the “Terminal” window. The program waits for you to enter your name, as shown in Figure 6.
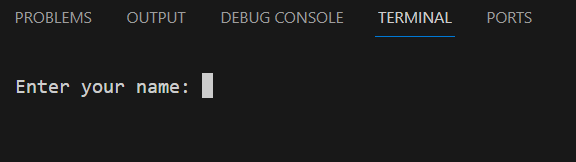
Type your name and hit the “Enter ⤶” key. Once you do that, your computer continues to execute the rest of the statements. When execution is complete, the final output is as shown in Figure 7.